Achilles Tendinopathy: Comprehensive Management Strategies for Relief and Recovery
Achilles tendinopathy is an overuse injury that can impair physical activities and lead to persistent discomfort. Often people will express pain upon taking their first steps in the morning or after long periods of standing or walking. Like a lot of tendon pain, in the initial stages the pain in often worst when first starting activity and tends to “warm up”. As the issue becomes more chronic we start to see more changes and the pain becomes more persistent. There are multiple factors with developing this condition but some commonalities are;
-“Too much, too soon” – big spikes in loading after relative inactivity – think getting back into summer shape after winter and smashing multiple gym classes
-Age-related collagen degradation – as we get older our collagen tissues can lose integrity and resilience and often our activity levels are much less
-Metabolic issues – conditions such as diabetes and metabolic syndromes can have negative impact on the strength of our tendons and connective tissue
-Calf muscle weakness and tightness – it is well established that calf muscle strength is a factor in developing achilles tendon issues
In managing this condition, it’s crucial to understand the multifaceted approach that encompasses various facets of treatment. There are two main types of Achilles tendinopathy – midportion and insertional. We’ll delve into the essentials of physical therapy, choosing proper footwear, employing progressive loading exercises, pain management and load tolerance to alleviate pain and speed up recovery.
Understanding Achilles Tendinopathy
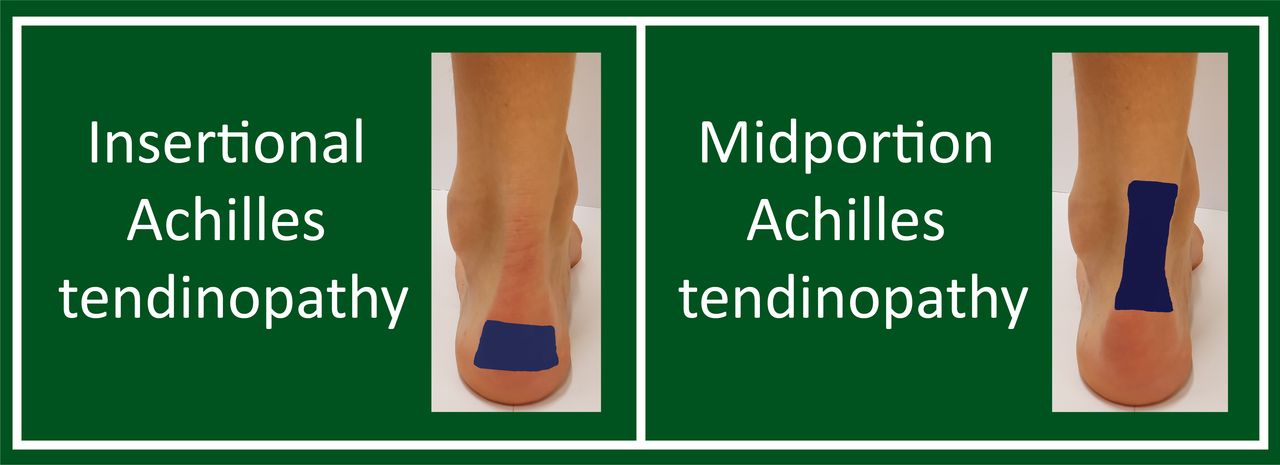
Achilles tendinopathy, comprising both mid-portion and insertional tendinopathy, is characterized by chronic tendon damage due to repetitive stress. To effectively manage this condition, it’s essential to differentiate between the two types:
-
Mid-Portion Tendinopathy: Affecting the mid-portion of the Achilles tendon, this form typically results in swelling, stiffness, and pain in that region.
-
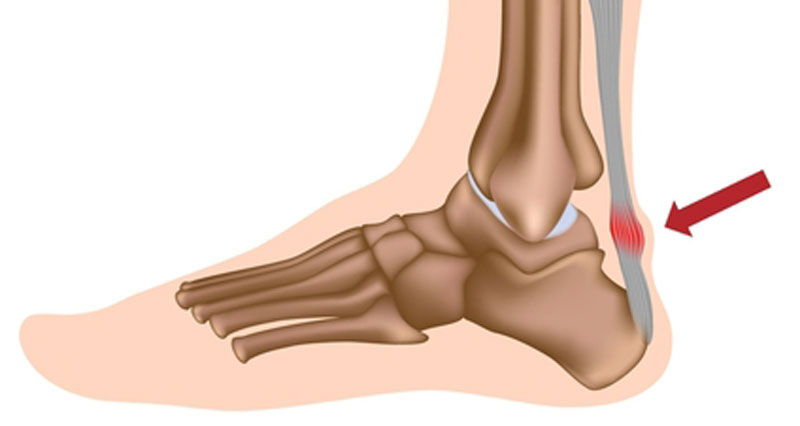
Insertional Tendinopathy: This variant manifests at the attachment point of the Achilles tendon to the calcaneus (heel bone), leading to pain and tenderness at the back of the heel.
Comprehensive Treatment Focus
-
Avoiding Excessive Dorsiflexion:
- Insertional Tendinopathy: To alleviate tendon compression against the calcaneus, steer clear of dorsiflexion that directly affects this area. Activity modifications and proper footwear are vital considerations.
-
Footwear Selection:
- Mid-Portion Tendinopathy: Choose footwear offering substantial cushioning, particularly at the posterior heel. Proper padding mitigates Achilles tendon impact during movement.
- Insertional Tendinopathy: Select shoes with generous heel padding to reduce discomfort and support healing. Ill-fitting or inadequately cushioned footwear can worsen the condition.
- Use of heel lifts – the use of a small heel lift such as 4mm or 6mm can be a great way to relieve strain and tension on the achilles and make walking and running much more comfortable, this can be placed under the shoe insole
-
Progressive Loading with Calf Raises:
- Both Types of Tendinopathy: Incorporate progressive loading through heavy calf raises with an eccentric emphasis to strengthen calf muscles and the Achilles tendon. This enhances tissue resilience and promotes healing. This should be done within pain tolerance and not exceeding more than 3/10 pain
-
Keeping the Tendon Warm:
- Both Types of Tendinopathy: Maintaining warmth in the Achilles tendon can be beneficial. Use compression sleeves or wraps to keep the area warm, especially during physical activities. Alternatively, a heat pack can be fantastic to get or keep the area warm around activity or for pain relief
-
Maintaining Activity within Load Tolerance:
- Both Types of Tendinopathy: Keep active during rehabilitation, but stay within your load tolerance. Avoid activities that aggravate symptoms and gradually increase intensity as the tendon heals. Make sure you are warming up thoroughly, and be conscious that your load capacity might limit how much you can do. As long as the flare up of pain is no longer than 24 hours it is usually fine but be conscious of doing too much.
-
Isometric Exercises:
- Both Types of Tendinopathy: Isometric exercises play a crucial role in pain management and loading without worsening symptoms. These exercises engage muscles without causing tendon movement, aiding in pain relief and maintaining muscle strength.
- Holding the top position of a calf raise can reduce pain, warm-up the tendon and be a great starting point for strengthening that is essential for long-term improvement (try 3 sets of 25 to 30 seconds)
- Shockwave Therapy – this can be a great adjunctive therapy to improve pain and reduce nerve sensitisation, promote collagen regeneration of healthy tissue and enhance blood flow and circulation. It is ideal for more chronic tendinopathies such as those that have been around for 3-6 months or longer
Achilles tendinopathy management requires a multifaceted approach, integrating various strategies to alleviate pain and promote healing. Beyond avoiding excessive dorsiflexion, choosing appropriate footwear, and incorporating progressive loading exercises, it’s essential to keep the tendon warm, use heat therapy judiciously, remain active within load tolerance, and employ isometric exercises. By adopting this comprehensive approach under the guidance of a healthcare professional, you can enhance your chances of a successful recovery. With patience and perseverance, you’ll be on the path to returning to your favorite activities with reduced discomfort and improved function.
Book in today for an assessment if you have been dealing with achilles tendon pain